Cancer Types: Head and Neck Cancer
What is it?
Cancer located anywhere in/near the mouth, nose, lymph nodes, throat and such is all characterized as head and neck cancer. Most head and neck cancers are squamous cell carcinomas (SCC). SCC is an uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells arising from the squamous cells in the epidermis, the skin’s outermost layer. SCC is the second most common form of skin cancer.
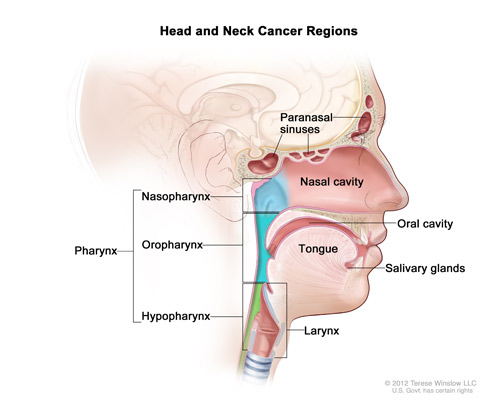
(Head and Neck Cancer Locations) Image by NIH National Cancer Institute {https://www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/head-neck-fact-sheet#q1}
Symptoms
The most common symptoms may include changes in the voice (hoarseness), trouble swallowing, sore throat that doesn’t heal, and lumps/sores that do not disappear. Pain in the ear(s) and mouth ulcer, among other things, are also symptoms of head and neck cancer but not as common.

(Lumps in the throat area) Image by Allied Academies { http://cancer.alliedacademies.com/events-list/wcc4}
If you find yourself with one of these symptoms, it’s recommended to see your doctor. Regular trips to your doctor, especially at an older age is the best way of finding cancer at an early stage. A doctor will check a person’s medical history, perform physical examination, and order diagnostic tests. The exams and tests may vary depending on the symptoms.
If the diagnosis is cancer, the doctor will try to figure out the stage of cancer it is currently at. Staging helps doctor find out if the cancer has spread and, if so, to which parts of the body. Some staging procedures involve an examination under anesthesia (in an operating room), x-rays, and other imaging and laboratory tests. Knowing the stage of the disease helps the doctor plan treatment.
Treatment
Creating a treatment plan varies from each individual patient. Depending on the location and stage of the cancer, possible treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. A combination of treatment might also be created.
Expanded explanations of treatment options here:
Radiation Therapy: https://radtecmedicaldevices.com/treatments-part-one-radiation-therapy/
Surgical Therapy: https://radtecmedicaldevices.com/treatments-part-two-surgical-therapy/
Chemotherapy: https://radtecmedicaldevices.com/treatments-part-three-chemotherapy/
Prevention
There are many different factors that can increase the risk of head and neck cancer. Reducing or negating these risk factors will lower the odds of cancer.
Tobacco users (both smoke and smokeless tobacco) are at a high risk of head and neck cancer. Not only does tobacco cause cancer for oneself but secondhand smoke can affect those around and are at greater risk. Alcohol can also lead to head and neck cancer. Combining both tobacco and alcohol is the most common risk factors of head and neck cancer. At least 75% of head and neck cancer patients are users of both tobacco and alcohol.
People with human papillomavirus (HPV), especially HPV type 16 is a risk factor for some types of head and neck cancers. Avoiding oral HPV infection may reduce the risk of HPV-associated head and neck cancers. Reducing your risk of HPV infection by receiving the HPV vaccine.
For those who have had head and neck cancer before, or any form of cancer, regular follow-up care is very important after treatment to make sure that the cancer has not returned, or that a second primary (new) cancer has not developed.
“Head and Neck Cancer Introduction.” Cancer.net, www.cancer.net/cancer-types/head-and-neck-cancer/view-all.
“Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC).” Skin Cancer Foundation, www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/squamous-cell-carcinoma.
“Head and Neck Cancers.” NIH National Cancer Institute, www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/head-neck-fact-sheet.

